
Introduction
Welcome! This document explains how to integrate with Criteo’s Direct Bidder solution to start your Criteo campaign. Criteo provides a piece of code to be added in the header of your pages. This generates an asynchronous call that allows Criteo to process the request and, where applicable, recognize users via supported identifiers, and return a set of bids and creatives.
Criteo will respond with the bid price in CPM along with the creative code or raw assets in case of native demand.
Requirements
You will receive from Criteo:
The endpoint URL
A list of identifiers for each ad placement and/or format you have available on the page
Code samples demonstrating how to initialize the Criteo tag and how to map the placements
Creative codes to be used in the adserver or directly on the page
We will need you to:
Implement the scripts on the page header
Map the placements available on each page and use it to initialize our tags
Criteo complies with the IAB Consent Framework. Please refer to their documentation for more information and examples of certified CMPs.
CDB Script - Loader
This code initializes the Criteo tags. The code will load the publishertag.js library and will also build the events queue that will be used later. The loader request is asynchronous and is cached on the user browser. No code changes are required on this section.
CDB Script - Placement mapping info
Bid Request - Passing bid price floors
You can set bid price floors in the ad unit declaration by adding an extension object to the placements declared, as placements[].ext.floors. You can set floors per media type and per size as in the example on the left. You can use the wildcard character (“*”) to define a default floor for all sizes. Make sure to specify the currency in which the floor is expressed via the “currency” field, please note it is required and not specifying it will result in the floor being discarded and thus ignored.
User ID Collection
To enrich the bid request data with user IDs (1st Party user IDs, 3rd Party IDs or hashed emails), please use the function Criteo.SetIdentities as described in the sections below.
This function accepts an array of OpenRTB EIDS objects as input:
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
source | String | Identifier source URL (publisher URL or vendor URL). |
uids[].id | String | User identifier |
uids[].atype | Integer | Identifier type. |
uids[].ext.stype | String | ID Source type. |
uids[].ext.persistence | String | (Optional, Criteo-specific) |
User ID Collection - First Party IDs
Use the function Criteo.SetIdentities providing the data below (examples on the right):
source: your domain
id: the user identifier
atype: Must be
1for cookie/device-based ID, must be3for person-based ID (e.g.: authenticated user ID, login ID, CRM/customer ID)ext.stype:
ppuidext.persistence:
jsorhttp
User ID Collection - Third Party IDs
Use the function Criteo.SetIdentities providing the data below (examples on the right):
source: the third-party solution domain
id: the user identifier
(recommended) atype:
1for cookie/device based ID,3for person-based ID (e.g.: authenticated user ID, login ID, CRM/customer ID)(optional) ext.persistence:
jsorhttp
User ID Collection - Hashed Emails
Use the function Criteo.SetIdentities providing the data below (examples on the right):
(optional) source: your domain or the domain of the solution operating on your behalf
id: the user data
atype:
3ext.stype: hashing algorithm used:
hemsha256,hemmd5,hemsha256md5. Please refer to next section for details on hashing formats.
Hashing formats
The hashing should be the users’ email address:
Encoded in UTF-8
Trimmed of any white space (eg: “test@criteo.com “ should become “test@criteo.com”)
Converted to lowercase
Hashed with MD5/SHA256/SHA256(MD5) & output as ASCII text
Example:
Type: String
Original Email: john.doe@gmail.com
SHA256: 375320dd9ae7ed408002f3768e16cb5f28c861062fd50dff9a3bff62e9dce4ef
MD5: e13743a7f1db7f4246badd6fd6ff54ff
SHA256 of MD5: 000e3171a5110c35c69d060112bd0ba55d9631c7c2ec93f1840e4570095b263a
Helpful links: https://www.miraclesalad.com/webtools/md5.php and https://www.miraclesalad.com/webtools/sha256.php
User ID Collection - Phone Numbers
Use the function Criteo.SetIdentities providing the data below (example on the right):
(optional) source: your domain or the domain of the solution operating on your behalf.
id: the user data
atype:
3ext.stype:
pnsha256Please refer to next section for details on hashing formats.
HASHED PHONE NUMBERS
Criteo uses SHA256 as a hashing method. The expected underlying phone numbers format is trimmed E.164 format, including the country code, without the leading "+" sign (so only 15 digits, at most): sha256(internationalPhoneNumber.replaceAll(/[^0-9]/g, "")).
Example:
1 (234) 567-8910 → sha256(12345678910) → 63640264849a87c90356129d99ea165e37aa5fabc1fea46906df1a7ca50db492
81-12-3456-7891 → sha256(811234567891) → d9825fb05347d3c910fc5202c0c20d07a87b791cc643c6f2d70402394a849540
02 1234 5678 → sha256(0212345678) → 826f54894e28f3f1795f3c5e3335cf98709c5d5b38b3f9c6d72467d491f032df
+33 1 40 40 22 90 → sha256(33140402290) → fda66831d0cb0eb4bffb21bc795308d69921c211c57be0ae15702071e3b9e988
CLEAR PHONE NUMBERS
Clear or unhashed phone numbers are not supported and must not be sent.
Tag on page integration
This code must be placed after the div element of each placement declared on the header. Please notice that the div/adunit names (ad-unit-0 and ad-unit-1 on this example) must be the exact same as the one declared on the header script.
The function Criteo.Passback.RenderAd(slotId,passback) will retrieve and display a bid for the given adunit otherwise, it will pass back.
Parameter | Type | Mandatory | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
slotid | string | yes | The slot id (div id) to be rendered | none |
passback | function | no | A function defining the passback in case of no bid. The passback sends the slotid as the parameter. Passback code must be an asynchronous javascript code. | none |
If you already have other ad tags on your page, you will need to move them to the passback input. You will find one example later in this document.
You must ensure that your passback code is compatible on asynchronous mode.
Example - Test page
You can see this example running on this page.
Explanation
LOADER
The first portion of the script loads the Criteo publisher tag
MAPPING
The second part maps the two ads available on the page (named adunit1 and adunit2) to their respective Criteo zoneid. This mapping is then submitted to Criteo, who will answer with an individual bid for each adunit.
RENDERING
The last portion of the code is implemented on the placement where the ads should be rendered. If Criteo has a bid for the adunit, the Criteo banner will be rendered inside the declared div. Otherwise, the tag will trigger the passback code provided as input.
This passback code in particular, appends one script and one ad tag inside the original div, resulting in the following structure:
<div id="adunitid1">
<script type="text/javascript" async="" src="//www.mydomain.com/mypassbackcode.js"></script>
<ad class="ads" style="display:inline-block;width:300px;height:250px" id="123"></ad>
</div>
You can take this example to adapt your current HTML tags.
Once again, you must ensure that your passback is compatible with an asynchronous environment.
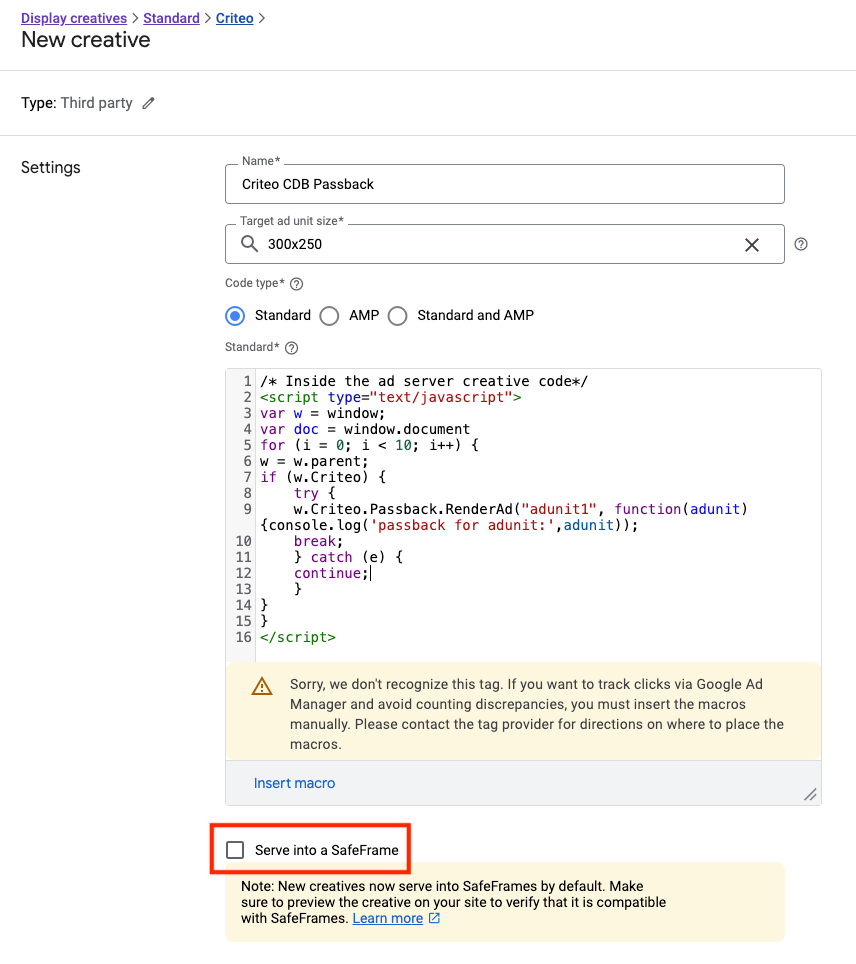
Set up as ad server tag
Please ensure that the creatives are not delivered in safe-frames (i.e. cross-domain iframes) as this code needs to retrieve the creatives stored on the main page. This code also relies on the function Criteo.Passback.RenderAd that accept the same inputs:
Parameter | Type | Mandatory | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
slotid | string | yes | The slot id (div id) to be rendered | none |
passback | function | no | A function defining the passback in case of no bid. The passback sends the slotid as a parameter. Passback code must be an asynchronous javascript code. | none |

Set up as ad server tag - in Google Ad Manager
The rendering code can be injected directly into a GAM creative as per example below. The “Serve into a SafeFrame” checkbox needs to be unchecked.
Native Ads - Native Placement
In order to activate Native demand, first, you need to declare a callback function that will be used to render the Native ad. This provides instructions on how the function Criteo.Passback.RenderAd() should build the native ad.
Native Ads - Native Object
When a native demand is available, Criteo will respond to the following native object:
NATIVE OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
product | Product object Array | List of product assets. |
advertiser | Includes the adv name and logo | |
privacy | Includes Ad Choices and opt-out URL | |
impression_pixels | Impression pixels object Array | List of impression pixels |
PRODUCT OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title | String | Product title. |
description | String | Product description. |
price | String | Product formatted price. It comes formatted by default with the currency symbol. |
click_url | String | Product landing page |
call_to_action | String | Product CTA |
image | Product image (400x400 px) |
IMAGE OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
url | String | Image URL. |
height | Integer | Image height |
width | Integer | Image width |
ADVERTISER OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
description | String | Advertiser name |
domain | String | Advertiser domain |
logo | Advertiser logo (200x200 px) |
PRIVACY OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
optout_click_url | String | Opt-out landing page URL |
optout_image_url | String | Ad Choices icon URL |
IMPRESSION PIXEL OBJECT
Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
url | String | Impression pixel beacon |
Native Ads - Ad requirements
Criteo Native guidelines:
Display the Ad Choices icon and implement the link to the opt-out page
Display at least one advertiser information (domain, name)
Display at least one product recommendation
Use Criteo to click URLs
Every impression pixel must be called once the ad is delivered
You will find to the right one sample code that uses the most relevant assets.

Native Ads - Product images
Criteo images for native inventory will be sized to fit within a 400x400 html element. They will not be padded to fit the dimensions or ratio; they should, therefore, be centered in the layout by the partner.

Native Ads - Adserver integration
The campaigns are configured as the normal campaign and you can reuse the same Creative codes for the standard ads. The Criteo.Passback.RenderAd() function will automatically identify the native ad context and execute whatever has been defined at the nativeCallback parameter.
Native Ads - Complete example
You will find a full example on this page. Please check the source-code.
